
Building an App-To-Phone Call Using Android and Flutter
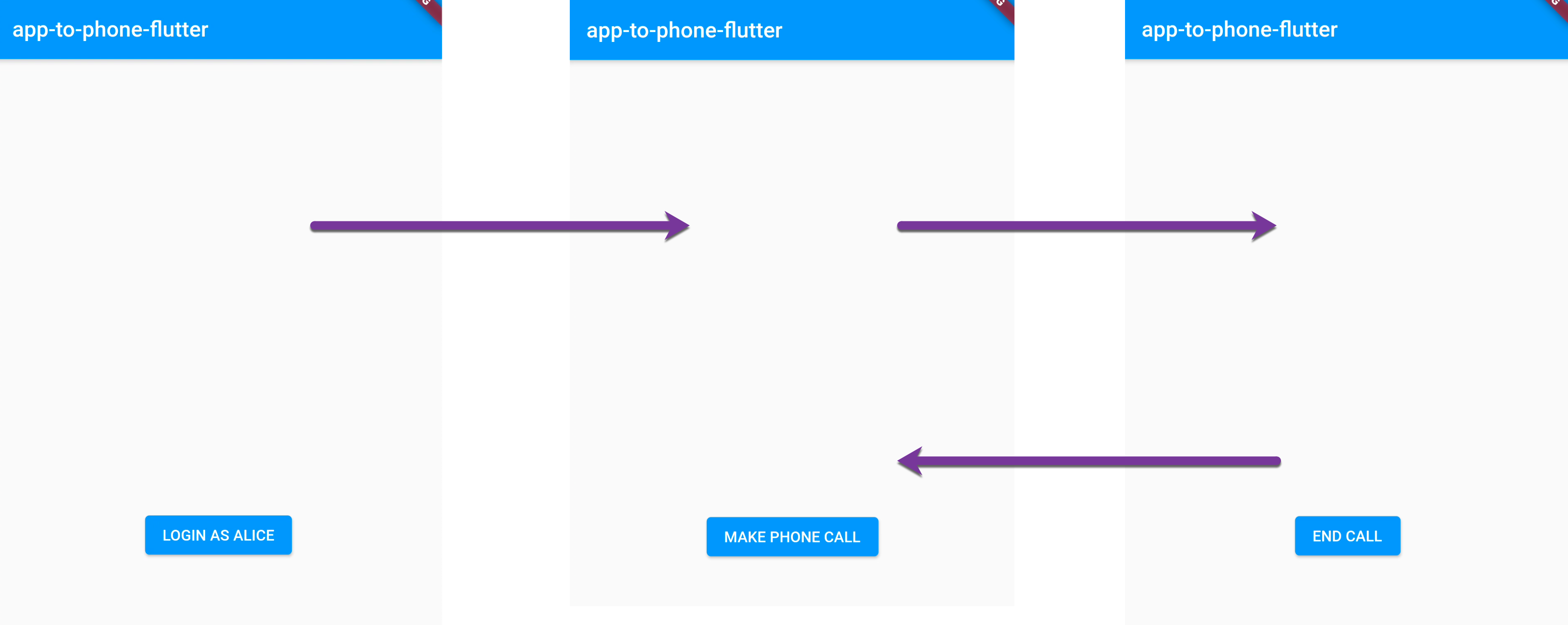
Today we will build an Android application using Flutter and utilize Vonage Client SDK to make a call from a mobile application to the phone. The application will have 3 screens (3 UI states):
Prerequisites
The source code is available on GitHub.
Before we begin building the application for our Android device, you'll need to prepare with the following prerequisites:
- Create a Call Control Object (NCCO)
- Install Nexmo CLI
- Setup Vonage application
- Install Flutter SDK
- Create a Flutter project
Vonage Application
Create An NCCO
A Call Control Object (NCCO) is a JSON array that we use to control the flow of a Voice API call. More information on NCCO can be found here here.
The NCCO needs to be public and accessible by the internet. To accomplish this, in this tutorial you'll be using GitHub Gist which provides a convenient way to host the configuration. Let's add a new gist:
- Go to https://gist.github.com/ (you have to be logged in into Github)
- Create a new gist with
ncco.jsonthe as filename - Copy and paste the following JSON object into the gist:
[
{
"action": "talk",
"text": "Please wait while we connect you."
},
{
"action": "connect",
"endpoint": [
{
"type": "phone",
"number": "PHONE_NUMBER"
}
]
}
]
- Replace
PHONE_NUMBERwith our phone number (Vonage numbers are in E.164 format https://developer.nexmo.com/concepts/guides/glossary#e-164-format, '+' and '-' are not valid. Make sure we specify our country code when entering our number, for example, US: 14155550100 and UK: 447700900001) - Click the
Create secret gistbutton - Click the
Rawbutton - Take note of the URL shown in our browser, we will be using it in the next step
Install Nexmo CLI
The Nexmo CLI allows us to carry out many operations on the command line. If we want to carry out tasks such as creating applications, purchasing Vonage numbers and so on, we will need to install the Nexmo CLI.
Nexmo CLI requires node.js, so we will need to install node.js first using these instructions.
To install the Beta version of the CLI with NPM run this command:
npm install nexmo-cli@beta -g
Set up the Nexmo CLI to use our Vonage API Key and API Secret. we can get these from the settings page in the Dashboard.
Run the following command in a terminal, while replacing api_key and api_secret with our own:
nexmo setup api_key api_secret
Setup Vonage Application
- Create our project directory if you've not already done so, run the following command in our terminal:
mkdir vonage-tutorial
2. Change into the project directory:
cd vonage-tutorial
- Create a Vonage application by copying and pasting the command below into the terminal Make sure to change the value of
--voice-answer-urlargument by replacingGIST-URLwith the gist URL from the previous step.
nexmo app:create "App to Phone Tutorial" --capabilities=voice --keyfile=private.key --voice-event-url=https://example.com/ --voice-answer-url=GIST-URL
Make a note of the Application ID that is echoed in our terminal when our application is created.
NOTE: A hidden file named
.nexmo-appis created in our project directory and contains the newly created Vonage Application ID and the private key. A private key file namedprivate.keyis also created.
Create User
Each participant is represented by a User object and must be authenticated by the Client SDK. In a production application, we would typically store this user information in a database.
Execute the following command to create a user called Alice
nexmo user:create name="Alice"
Generate JWT
The JWT is used to authenticate the user. Execute the following command in the terminal to generate a JWT for the user Alice.
In the following command replace the APPLICATION_ID with the ID of our application:
nexmo jwt:generate sub=Alice exp=$(($(date +%s)+86400)) acl='{"paths":{"/*/users/**":{},"/*/conversations/**":{},"/*/sessions/**":{},"/*/devices/**":{},"/*/image/**":{},"/*/media/**":{},"/*/applications/**":{},"/*/push/**":{},"/*/knocking/**":{},"/*/legs/**":{}}}'
The command above sets the expiry of the JWT to one day from now, which is the maximum.
Make a note of the JWT we generated for Alice.
NOTE: In a production environment, our application should expose an endpoint that generates a JWT for each client request.
Install Android Studio
Download and install Android Studio.
Flutter Setup
Install Flutter SDK
This step will vary on MacOS, Win, and Linux, but in general, it boils down to downloading flutter SDK for a given OS, extracting the SDK file, and adding the sdk\bin folder to the system PATH variable. Detailed instruction can be found here.
Fortunately, flutter comes with a tool that allows us to verify if SDK and all required "components" are present and configured correctly. Run this command:
flutter doctor
Flutter Doctor will verify if Flutter SDK is installed and other components are installed and configured correctly. If problems will be detected we will see the description and hint regarding the fix.
Install the Flutter Plugin
Open Android Studio, go to Preferences | plugins and Install Flutter and Dart plugins from the marketplace.
Flutter plugin will add a new toolbar that allows to run and debug Flutter application:
Create the Flutter Project
You will create a Flutter project using Android Studio.
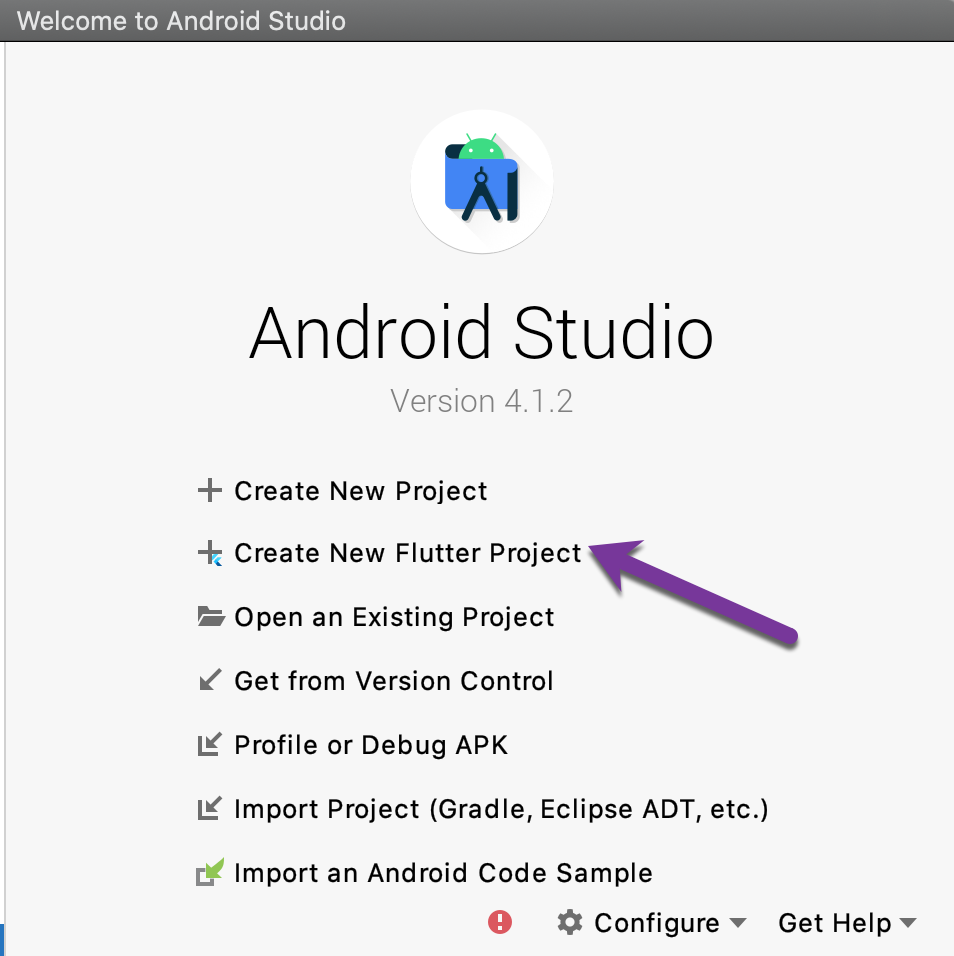
- Run Android Studio
- On the Android Studio welcome screen select
Create New Flutter project
- Select
Flutter Applicationand clickNext - Enter
app_to_phone_flutteras project name, enterFlutter SDK pathand clickNext - Select
Include Kotlin support for Android codeand clickFinish
Notice that
app_to_phone_flutterfolder (flutter project) containsiosfolder containing the OS project andiosfolder containing the iOS project.
Connect Android device or emulator and run the app to verify that everything works as expected.
Two-way Flutter/Android Communication
Currently, Client SDK is not available as a Flutter package, so we will have to use Android native Client SDK and communicate between Android and Flutter using MethodChannel - this way, Flutter will call Android methods, Android will call Flutter methods.
Flutter code will be stored in the lib/ain.dart file, while Android native code will be stored in the android/app/src/main/kotlin/com/example/app_to_phone_flutter/MainActivity.kt file.
Init Flutter Application
Flutter applications are built using a programming language called Dart.
Open lib/main.dart file, and replace all of the contents with the following code:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
home: CallWidget(title: 'app-to-phone-flutter'),
);
}
}
class CallWidget extends StatefulWidget {
CallWidget({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
_CallWidgetState createState() => _CallWidgetState();
}
class _CallWidgetState extends State<CallWidget> {
SdkState _sdkState = SdkState.LOGGED_OUT;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(widget.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
SizedBox(height: 64),
_updateView()
],
),
),
);
}
Widget _updateView() {
if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_OUT) {
return ElevatedButton(
child: Text("LOGIN AS ALICE")
);
}
}
Future<void> _loginUser() async {
// Login user
}
Future<void> _makeCall() async {
// Make call
}
Future<void> _endCall() async {
// End call
}
}
enum SdkState {
LOGGED_OUT,
LOGGED_IN,
WAIT,
ON_CALL,
ERROR
}
The above code contains custom CallWidget which will be responsible for managing the application state (logging the user and managing the call). The SdkState enum represents possible states of Vonage Client SDK. This enum will be defined twice - one for Flutter using Dart and one for Android using Kotlin. The widget contains the _updateView method that will change the UI based on SdkState value.
Run the application using the green arrow button on the Flutter toolbar:
We should see the Login Alice button:
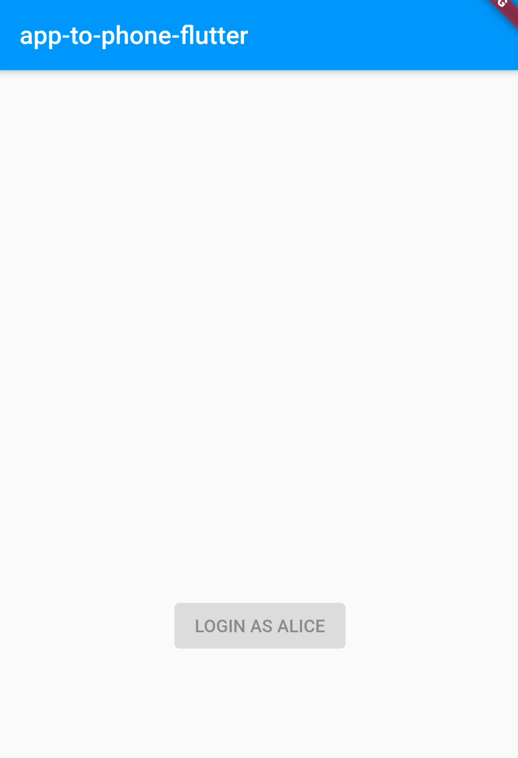
Login Screen
The Login as Aice button is disabled so now add onPressed handler to the ElevatedButton to allow logging in:
Widget _updateView() {
if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_OUT) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _loginUser(); },
child: Text("LOGIN AS ALICE")
);
}
}
Update body of _loginUser method to communicate with native code and login the user:
Future<void> _loginUser() async {
String token = "ALICE_TOKEN";
try {
await platformMethodChannel.invokeMethod('loginUser', <String, dynamic>{'token': token});
} on PlatformException catch (e) {
print(e);
}
}
Replace the ALICE_TOKEN with the JWT token, we obtained previously, to authenticate the user Alice from Vonage CLI. Flutter will call loginUser method and pass the token as an argument. The loginUser method defined in the MainActivity class (you will get there in a moment). To call this method from Flutter we have to define a MethodChannel. Add the platformMethodChannel field at the top of _CallWidgetState class:
class _CallWidgetState extends State<CallWidget> {
SdkState _sdkState = SdkState.LOGGED_OUT;
static const platformMethodChannel = const MethodChannel('com.vonage');
The com.vonage string represents the unique channel id that we will also refers to the native Android code (MainActivity class). Now we need to handle this method call on the native Android side.
Open MainActivity class. Note that the Flutter plugin displays a hint to open this Android project in the separate instance of Android Studio (another window). Do so to have better code completion for the Android project:
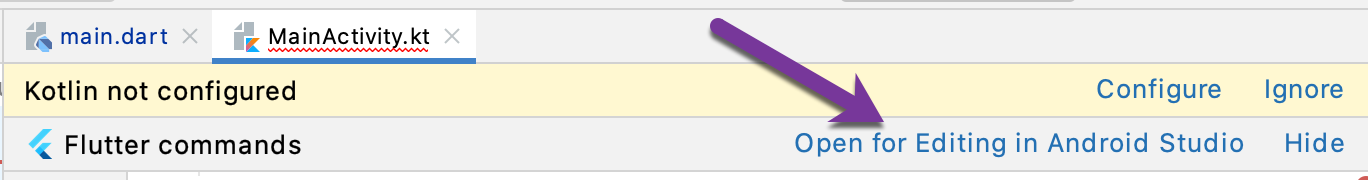
NOTE: This happens because the Flutter project consists of the Android project and the iOS project.
To listen for method calls originating from Flutter add addFlutterChannelListener method call inside configureFlutterEngine method:
override fun configureFlutterEngine(@NonNull flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine)
addFlutterChannelListener()
}
Now add addFlutterChannelListener and loginUser methods inside the MainActivity class (same level as the above configureFlutterEngine method):
private fun addFlutterChannelListener() {
MethodChannel(flutterEngine?.dartExecutor?.binaryMessenger, CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
when (call.method) {
"loginUser" -> {
val token = requireNotNull(call.argument<String>("token"))
loginUser(token)
result.success("")
}
else -> {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
}
}
private fun loginUser(token: String) {
Log.d("TAG", "login with token: $token")
}
After running the application we should see login with token... message at Android Logcat. Now it's time to create a missing client.
Add Client SDK Dependency
Add a custom Maven URL repository to our Gradle configuration. Add the following maven block inside the allprojects block within the project-level build.gradle.kts file:
allprojects {
repositories {
google()
jcenter()
maven {
url "https://artifactory.ess-dev.com/artifactory/gradle-dev-local"
}
}
}
Now add the Client SDK dependency to the project in the app\build.gradle file:
dependencies {
// ...
implementation 'com.nexmo.android:client-sdk:2.8.1'
}
In the same file set min Android SDK version to 23:
minSdkVersion 23
Run Sync project with Gradle command in Android Studio, as shown in the example below:
Initialize Client
Open MainActivity class and add the client property which will hold the reference to the Nexmo client:
private lateinit var client: NexmoClient
Now add initClient method to initialise the client:
private fun initClient() {
client = NexmoClient.Builder().build(this)
}
To call the initClient method from the existing the configureFlutterEngine method, we're going to need to add the initClient() line as shown in the example below:
override fun configureFlutterEngine(@NonNull flutterEngine: FlutterEngine) {
super.configureFlutterEngine(flutterEngine)
initClient()
addFlutterChannelListener()
}
Login The User
Modify login method body to call login on the client instance:
private fun login(token: String) {
client.login(token)
}
This will allow us to log the user (Alice) in using Client SDK.
Notify Flutter About Client SDK State Change
To notify Flutter of any changes to the state in the SDK, you'll need to add enum to represents the states of the client SDK. You've already added the equivalent SdkState enum in the main.dart file). Add the followingSdkState enum, at the bottom of the MainActivity.kt file:
enum class SdkState {
LOGGED_OUT,
LOGGED_IN,
WAIT,
ON_CALL,
ERROR
}
Next, we need to add the connection listener and map some of the SDK states to SdkState enum. Modify the body of the initClient method as shown in the example below:
private fun initClient() {
client = NexmoClient.Builder().build(this)
client.setConnectionListener { connectionStatus, _ ->
when (connectionStatus) {
ConnectionStatus.CONNECTED -> notifyFlutter(SdkState.LOGGED_IN)
ConnectionStatus.DISCONNECTED -> notifyFlutter(SdkState.LOGGED_OUT)
ConnectionStatus.CONNECTING -> notifyFlutter(SdkState.WAIT)
ConnectionStatus.UNKNOWN -> notifyFlutter(SdkState.ERROR)
}
}
}
Finally, the notifyFlutter method needs to be added to the MainActivity class:
private fun notifyFlutter(state: SdkState) {
Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).post {
MethodChannel(flutterEngine?.dartExecutor?.binaryMessenger, "com.vonage")
.invokeMethod("updateState", state.toString())
}
}
Notice that we store the state in the enum, but we are sending it as a string. Communication with Flutter happens on the main thread, so we need to use Handler to switch threads. The MethodChannel will call updateState method defined in the main.dart file.
Retrieve SDK State By Flutter
To retrieve state updates in Flutter we have to listen for method channel updates. Open main.dart file and add these two methods inside _CallWidgetState class:
_CallWidgetState() {
platformMethodChannel.setMethodCallHandler(methodCallHandler);
}
Future<dynamic> methodCallHandler(MethodCall methodCall) async {
switch (methodCall.method) {
case 'updateState':
{
setState(() {
var arguments = 'SdkState.${methodCall.arguments}';
_sdkState = SdkState.values.firstWhere((v) {return v.toString() == arguments;}
);
});
}
break;
default:
throw MissingPluginException('notImplemented');
}
}
These methods receive the "signal" from Android and converts it to an enum. Now update the contents of the _updateView method to support SdkState.WAIT and SdkState.LOGGED_IN states, as shown in the example below:
Widget _updateView() {
if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_OUT) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _loginUser(); },
child: Text("LOGIN AS ALICE")
);
} else if (_sdkState == SdkState.WAIT) {
return Center(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(),
);
} else if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_IN) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _makeCall(); },
child: Text("MAKE PHONE CALL")
);
}
}
During SdkState.WAIT the progress bar will be displayed. After successful login application will show the MAKE PHONE CALL button.
NOTE: While modifying Android native code Flutter hot reload will not work. we have to stop the application and run it again.
Run the app and click the button labelled LOGIN AS ALICE. The MAKE PHONE CALL button should appear, which is another state of the Flutter app based on the SdkState enum`). An example of this is shown in the image below:
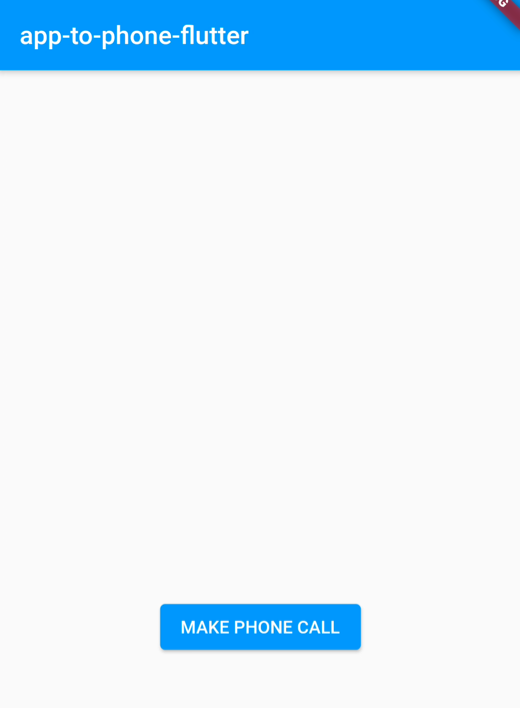
Make A Call
We now need to add functionality to make a phone call. Open the main.dart file and update the body of the _makeCall method as shown below:
Future<void> _makeCall() async {
try {
await requestPermissions();
await platformMethodChannel
.invokeMethod('makeCall');
} on PlatformException catch (e) {
print(e);
}
}
The above method will communicate with Android so we have to update the code in MainActivity class as well. Add makeCall clauses to when statement inside addFlutterChannelListener method:
private fun addFlutterChannelListener() {
MethodChannel(flutterEngine?.dartExecutor?.binaryMessenger, "com.vonage").setMethodCallHandler { call, result ->
when (call.method) {
"loginUser" -> {
val token = requireNotNull(call.argument<String>("token"))
login(token)
result.success("")
}
"makeCall" -> {
makeCall()
result.success("")
}
else -> {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
}
}
Now in the same file add the onGoingCall property, which defines if and when a call is ongoing:
private var onGoingCall: NexmoCall? = null
NOTE: Currently the Client SDK does not store ongoing call reference, so we have to store it in
MainActivityclass. we will use it later to end the call.
Now in the same file add makeCall method:
@SuppressLint("MissingPermission")
private fun makeCall() {
notifyFlutter(SdkState.WAIT)
// Callee number is ignored because it is specified in NCCO config
client.call("IGNORED_NUMBER", NexmoCallHandler.SERVER, object : NexmoRequestListener<NexmoCall> {
override fun onSuccess(call: NexmoCall?) {
onGoingCall = call
notifyFlutter(SdkState.ON_CALL)
}
override fun onError(apiError: NexmoApiError) {
notifyFlutter(SdkState.ERROR)
}
})
}
The above method sets the state of the Flutter app to SdkState.WAIT and waits for the Client SDK response (error or success). Now we need to add support for both states (SdkState.ON_CALL and SdkState.ERROR) inside main.dart file (Flutter). Update body of the _updateView method to show the same as below:
Widget _updateView() {
if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_OUT) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _loginUser(); },
child: Text("LOGIN AS ALICE")
);
} else if (_sdkState == SdkState.WAIT) {
return Center(
child: CircularProgressIndicator(),
);
} else if (_sdkState == SdkState.LOGGED_IN) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _makeCall(); },
child: Text("MAKE PHONE CALL")
);
} else if (_sdkState == SdkState.ON_CALL) {
return ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () { _endCall(); },
child: Text("END CALL")
);
} else {
return Center(
child: Text("ERROR")
);
}
}
Each state change will result in UI modification. Before making a call the application needs specific permissions to use the microphone. In the next step, we're going to add the functionality in our project to request these permissions.
Request Permissions
The application needs to be able to access the microphone, so we have to request Android's android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO permission (Flutter calls it Permission.microphone).
First, we need to add the permission_handler package. Open pubspec.yaml file and add permission_handler: ^6.0.1+1 dependency under sdk: flutter:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
permission_handler: ^6.0.1+1
Indentation matters in
yamlfiles, so make surepermission_handleris at the same indentation level as theflutter:item.
Run the below command in the terminal to download the newly added Flutter package:
flutter pub get
At the top of the main.dart file, you'll need to import the permission_handler package as shown in the example below:
import 'package:permission_handler/permission_handler.dart';
To trigger the request for certain permissions, you'll need to add the requestPermissions() method within the _CallWidgetState class inside the main.dart file. So add this new method inside the class:
Future<void> requestPermissions() async {
await [ Permission.microphone].request();
}
Finally, we need to add two permissions (uses-permission tags) inside app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml file, above the application tag:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<application
...
NOTE:
android.permission.INTERNETpermission is granted implicitly by the Android, so we don't have to request it in Flutter explicitly.
Run the app and click MAKE PHONE CALL to start a call. The permissions dialogue will appear and after granting the permissions the call will start.
Remainder: we defined the phone number earlier in NCCO
The state of the application will be updated to SdkState.ON_CALL and the UI will be updated:
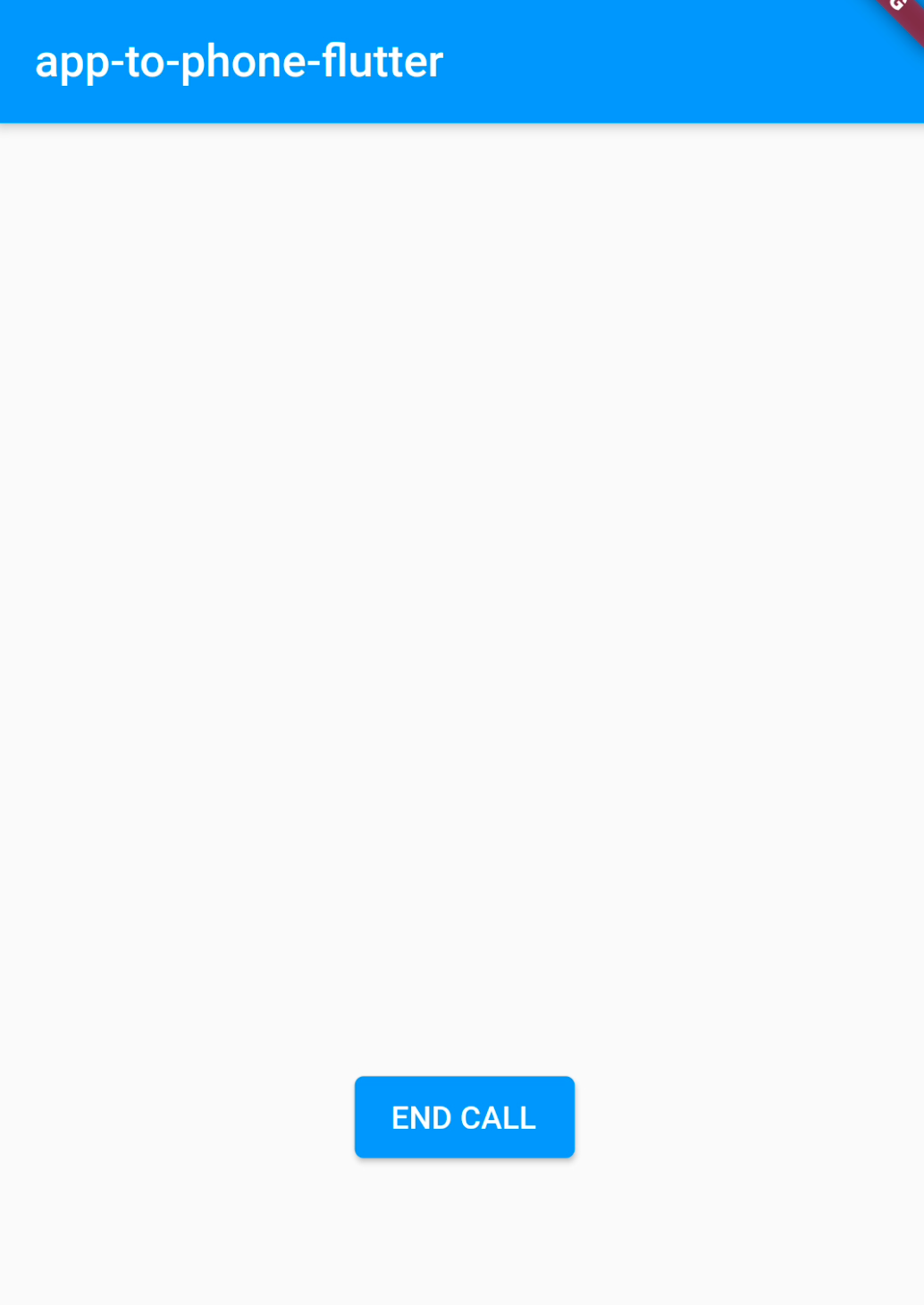
End the Call
To end the call we need to trigger the method on the native Android application using platformMethodChannel. Inside main.dart file update body of the _endCall method:
Future<void> _endCall() async {
try {
await platformMethodChannel.invokeMethod('endCall');
} on PlatformException catch (e) {}
}
The above method will communicate with Android so we have to update the code in the MainActivity class. Add endCall clauses to when statement inside the addFlutterChannelListener method:
when (call.method) {
"loginUser" -> {
val token = requireNotNull(call.argument<String>("token"))
login(token)
result.success("")
}
"makeCall" -> {
makeCall()
result.success("")
}
"endCall" -> {
endCall()
result.success("")
}
else -> {
result.notImplemented()
}
}
Now in the same file add the endCall method:
private fun endCall() {
onGoingCall?.hangup(object : NexmoRequestListener<NexmoCall> {
override fun onSuccess(call: NexmoCall?) {
onGoingCall = null
notifyFlutter(SdkState.LOGGED_IN)
}
override fun onError(apiError: NexmoApiError) {
notifyFlutter(SdkState.ERROR)
}
})
}
The above method sets the state of the Flutter app to SdkState.WAIT and waits for the response from the Client SDK, which can be either error or success. Both UI states are already supported in the Flutter application.
You have handled ending the call by pressing END CALL button in the Flutter application UI, however, the call can also end outside of the Flutter app e.g. the call will be rejected or answered and later ended by the callee (on the real phone).
To support these cases we have to add NexmoCallEventListener listener to the call instance and listen for call-specific events.
Define the callEventListener property at the top of the MainActivity class:
private val callEventListener = object : NexmoCallEventListener {
override fun onMemberStatusUpdated(callMemberStatus: NexmoCallMemberStatus, callMember: NexmoCallMember) {
if (callMemberStatus == NexmoCallMemberStatus.COMPLETED || callMemberStatus == NexmoCallMemberStatus.CANCELLED) {
onGoingCall = null
}
}
override fun onMuteChanged(mediaActionState: NexmoMediaActionState, callMember: NexmoCallMember) {}
override fun onEarmuffChanged(mediaActionState: NexmoMediaActionState, callMember: NexmoCallMember) {}
override fun onDTMF(dtmf: String, callMember: NexmoCallMember) {}
}
The onMemberStatusUpdated callback informs us the call has ended.
To register the above listener modify onSuccess callback inside makeCall method:
onGoingCall = call
onGoingCall?.addCallEventListener(callEventListener)
Finally, modify endCall method to unregister the callEventListener listener inside onSuccess callback:
onGoingCall?.removeCallEventListener(callEventListener)
onGoingCall = null
Run the app and if you've followed through this tutorial step by step, you'll be able to make a phone call from our mobile application to a physical phone number.
Summary
You have successfully built the application. By doing so we have learned how to make a phone call from a mobile application to the phone using Vonage Client SDK. For the complete version please see this project on GitHub. Check out the iOS equivalent of this blogpost.
To familiarize yourself with other use cases please see other tutorials and the Vonage developer center.