
How to Send WhatsApp Messages With Laravel
Take two things that we love: WhatsApp messages and Laravel framework. Mix them together. What do you get? Fun with phones!
This tutorial shows you how to create a Laravel application that sends and responds to WhatsApp messages.
You will need:
- A PHP development platform (Laravel 8 requires PHP 7.3 or later)
- WhatsApp on your phone
Vonage API Account
To complete this tutorial, you will need a Vonage API account. If you don’t have one already, you can sign up today and start building with free credit. Once you have an account, you can find your API Key and API Secret at the top of the Vonage API Dashboard.
Get the Code Running
The project is on GitHub at nexmo-community/laravel-messages, so go ahead and clone that repository to your computer.
Run the command composer install to get the dependencies needed for this project.
This application uses the phpdotenv library to manage its configuration on a dev platform. Copy the file .env.example to .env and edit the file as needed. In particular, you should update the NEXMO_API_KEY and NEXMO_API_SECRET lines at the end of the file to connect your Vonage account (we used to be called Nexmo, and old habits die hard!)
The application is ready to go! Start it with:
php artisan serve
By default, this will run your application on port 8000. Check that you have a Laravel homepage on http://localhost:8000 before moving on.
Set Up Ngrok
Since the application needs to be able to receive incoming webhooks for two-way messaging communication, we need a way to allow public URLs to access the dev platform. I usually use Ngrok for this; it's an excellent tool.
Start an Ngrok tunnel to port 8000 (or whatever port your application is running on):
ngrok http 8000
This starts an in-terminal console, so it looks something like this:
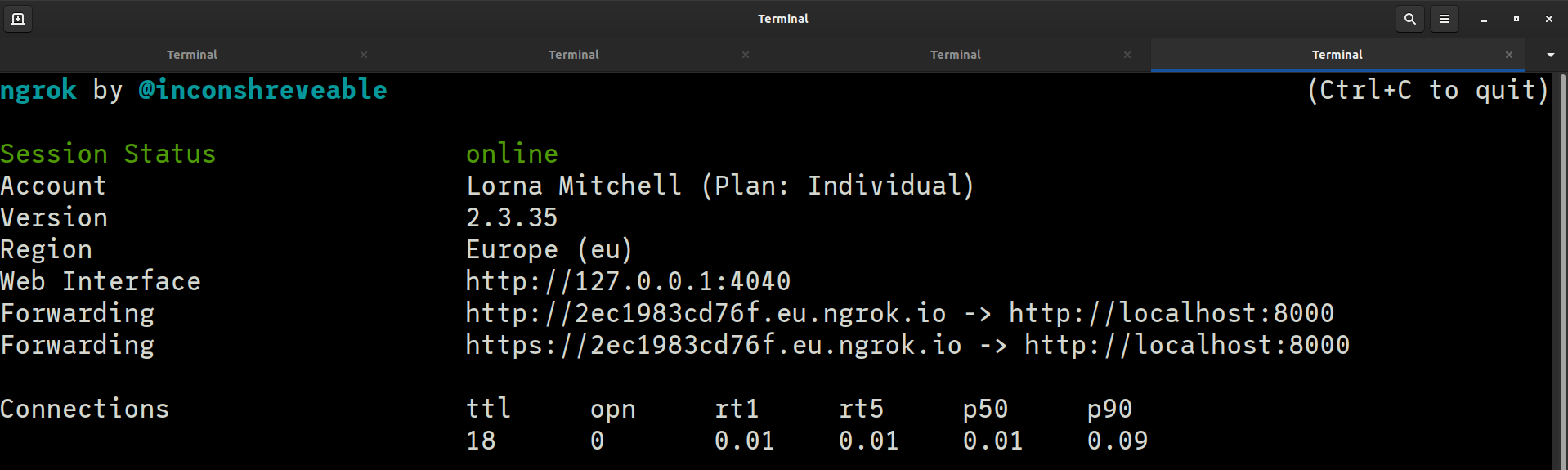
Copy the "Forwarding" https URL. We will need this shortly to configure the Vonage Messages API sandbox. You can also check everything is wired up by requesting this URL in your browser and seeing the same Laravel landing page as before.
Configure the Messages Sandbox
To get incoming WhatsApp messages directed to your application, we need to do a little bit of configuration in the dashboard. Under "Messages and Dispatch," click on "Sandbox" we will use the Messages API Sandbox for the demo today, but if you have a WhatsApp Business account, you could use the same approach to message any user without the Sandbox or whitelisting process.
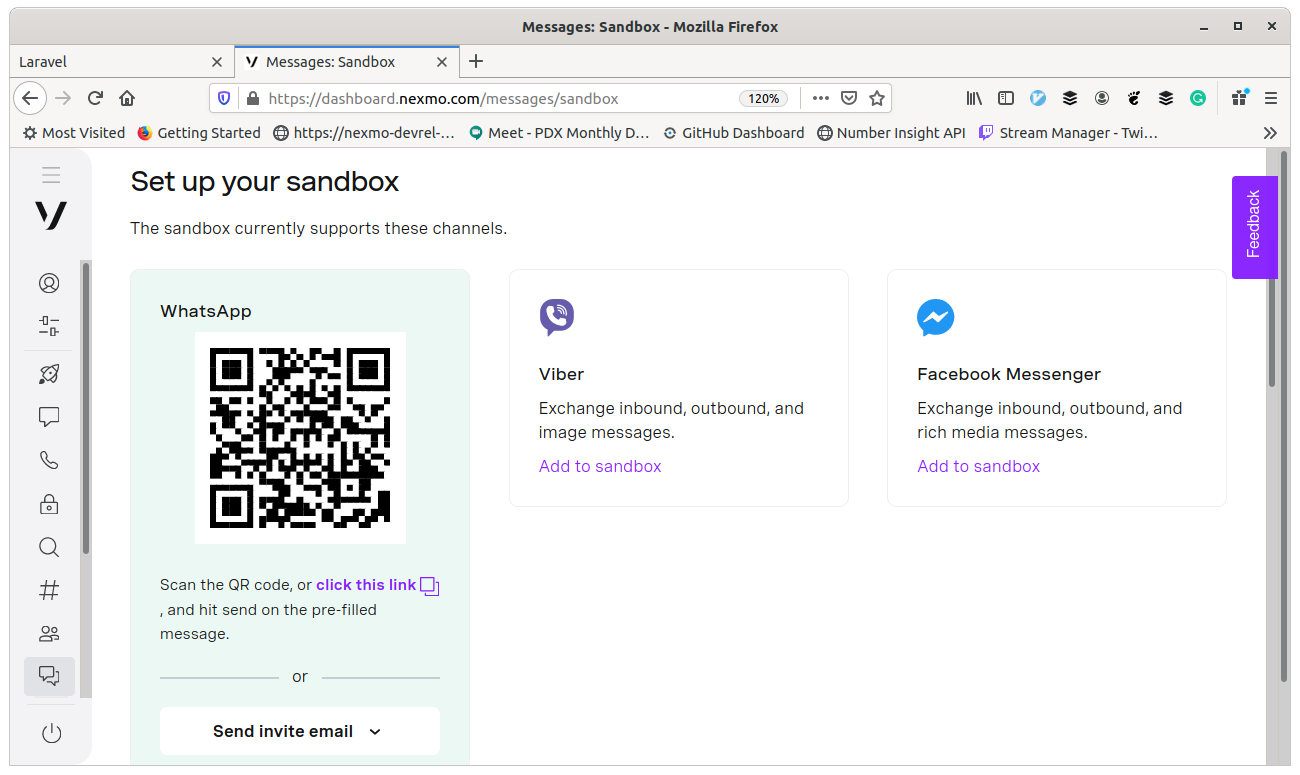
Add your phone number to the Sandbox by scanning the QR code or messaging the magic words to the number shown. I am not sure why I enjoy the magic words "auth method" so much, but it really seems like magic!
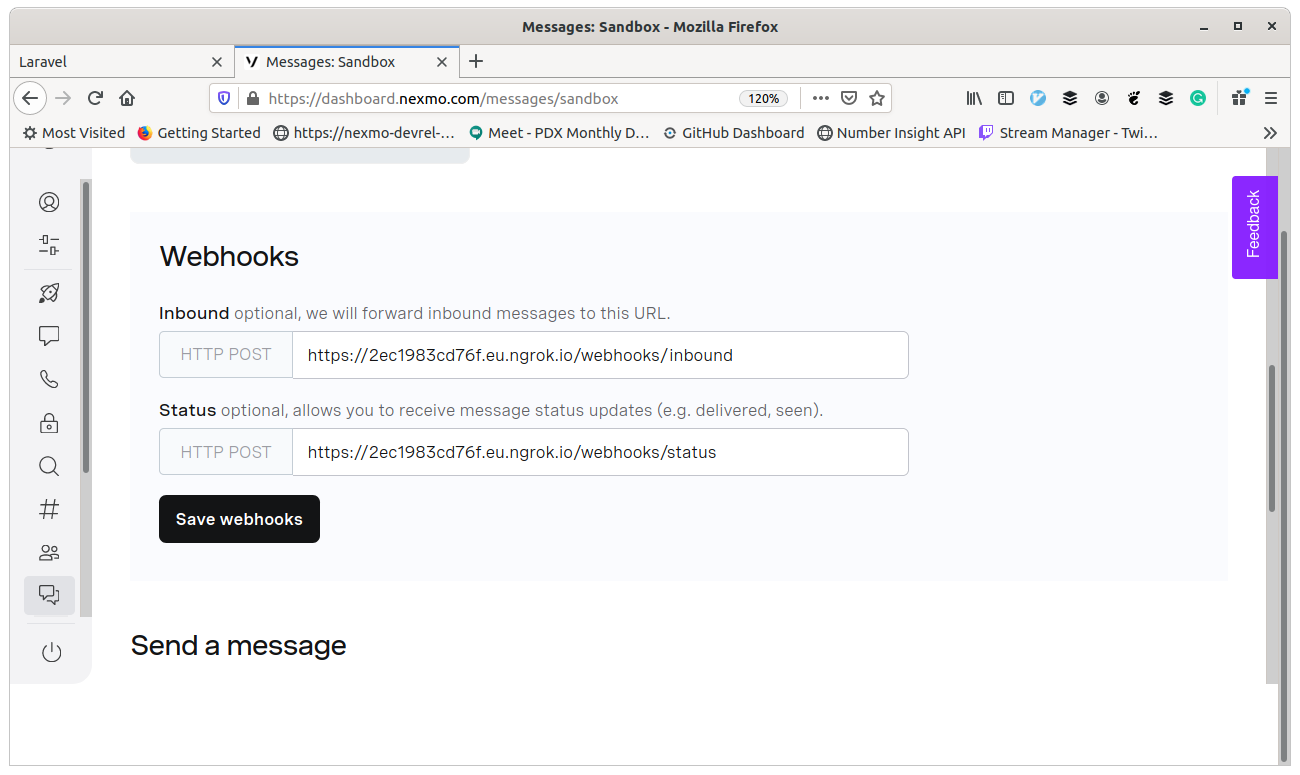
Time to configure the webhooks, and you will need the URL copied from the ngrok console earlier.
- Inbound should be
[url you copied earlier]/webhooks/inbound - Status should be
[url you copied earlier]/webhooks/status
Don't forget to press "Save" here! That seems to trip me up more often than it ought to.
Inside the Code
Let's look at the various routes set up in this application and how they interact with the Messages API.
Sending From Laravel
The best place to start with this application is at http://localhost:8000/messages where you can add your phone number and send yourself a message.
Note that the number needs to be in the international (E.164) format without a leading +. So for US numbers, start with 1 and then add the full number with area code. For the UK, start with 44 and then add the whole number without the leading 0.
Here's what happens when that form gets submitted:
// in routes/web.php
Route::post('/message', function(Request $request) {
// TODO: validate incoming params first!
$url = "https://messages-sandbox.nexmo.com/v0.1/messages";
$params = ["to" => ["type" => "whatsapp", "number" => $request->input('number')],
"from" => ["type" => "whatsapp", "number" => "14157386170"],
"message" => [
"content" => [
"type" => "text",
"text" => "Hello from Vonage and Laravel :) Please reply to this message with a number between 1 and 100"
]
]
];
$headers = ["Authorization" => "Basic " . base64_encode(env('NEXMO_API_KEY') . ":" . env('NEXMO_API_SECRET'))];
$client = new \GuzzleHttp\Client();
$response = $client->request('POST', $url, ["headers" => $headers, "json" => $params]);
$data = $response->getBody();
Log::Info($data);
return view('thanks');
});
This route uses Guzzle to send a POST request to the Messages Sandbox, and if the credentials are correct and the supplied phone number is whitelisted to the application, it will send the message you can see defined here. The message prompts the user to reply, so let's see that code next.
Receiving and Responding to WhatsApp Messages
With the webhooks configured in the dashboard and the Ngrok tunnel running, the local development application can receive incoming WhatsApp messages. If you already replied to the challenge to supply a number, then you know what happens next :)
Here's the code:
// in routes/web.php
Route::post('/webhooks/inbound', function(Request $request) {
$data = $request->all();
$text = $data['message']['content']['text'];
$number = intval($text);
Log::Info($number);
if($number > 0) {
$random = rand(1, 8);
Log::Info($random);
$respond_number = $number * $random;
Log::Info($respond_number);
$url = "https://messages-sandbox.nexmo.com/v0.1/messages";
$params = ["to" => ["type" => "whatsapp", "number" => $data['from']['number']],
"from" => ["type" => "whatsapp", "number" => "14157386170"],
"message" => [
"content" => [
"type" => "text",
"text" => "The answer is " . $respond_number . ", we multiplied by " . $random . "."
]
]
];
$headers = ["Authorization" => "Basic " . base64_encode(env('NEXMO_API_KEY') . ":" . env('NEXMO_API_SECRET'))];
$client = new \GuzzleHttp\Client();
$response = $client->request('POST', $url, ["headers" => $headers, "json" => $params]);
$data = $response->getBody();
}
Log::Info($data);
});
This example probably isn't exactly what you'd want your application to do, but it includes the moving parts you might need! The incoming webhook arrives, and we grab the data and try to read the message content as an integer. We do a little fun maths operation with a randomly generated number and send a reply to the user exactly as we did in the first code example.
You could also use the Laravel HTTP Client in place of Guzzle if you're more familiar with that. The Laravel HTTP Client is a wrapper for Guzzle.
Status Updates
Remember the status webhook we configured earlier? Events about the messages such as when they are submitted (sent from Vonage to WhatsApp), delivered (arrived on the user's device), and read (the user opened the message) are delivered to this endpoint. This application doesn't do a lot with them, but it is great to have access and be able to respond to them.
The status endpoints are also pretty handy for debugging. The route in the example application looks like this:
// in routes/web.php
Route::post('/webhooks/status', function(Request $request) {
$data = $request->all();
Log::Info($data);
});
So it just logs each event as it happens. Logging is incredibly valuable when debugging issues! By default, you can find these logs in storage/logs/laravel.log and it is well worth keeping an eye on what is happening in that file as you develop an application like this one!
Fun With Phones
If you didn't try it already, then go ahead and enjoy a WhatsApp chat with your application.
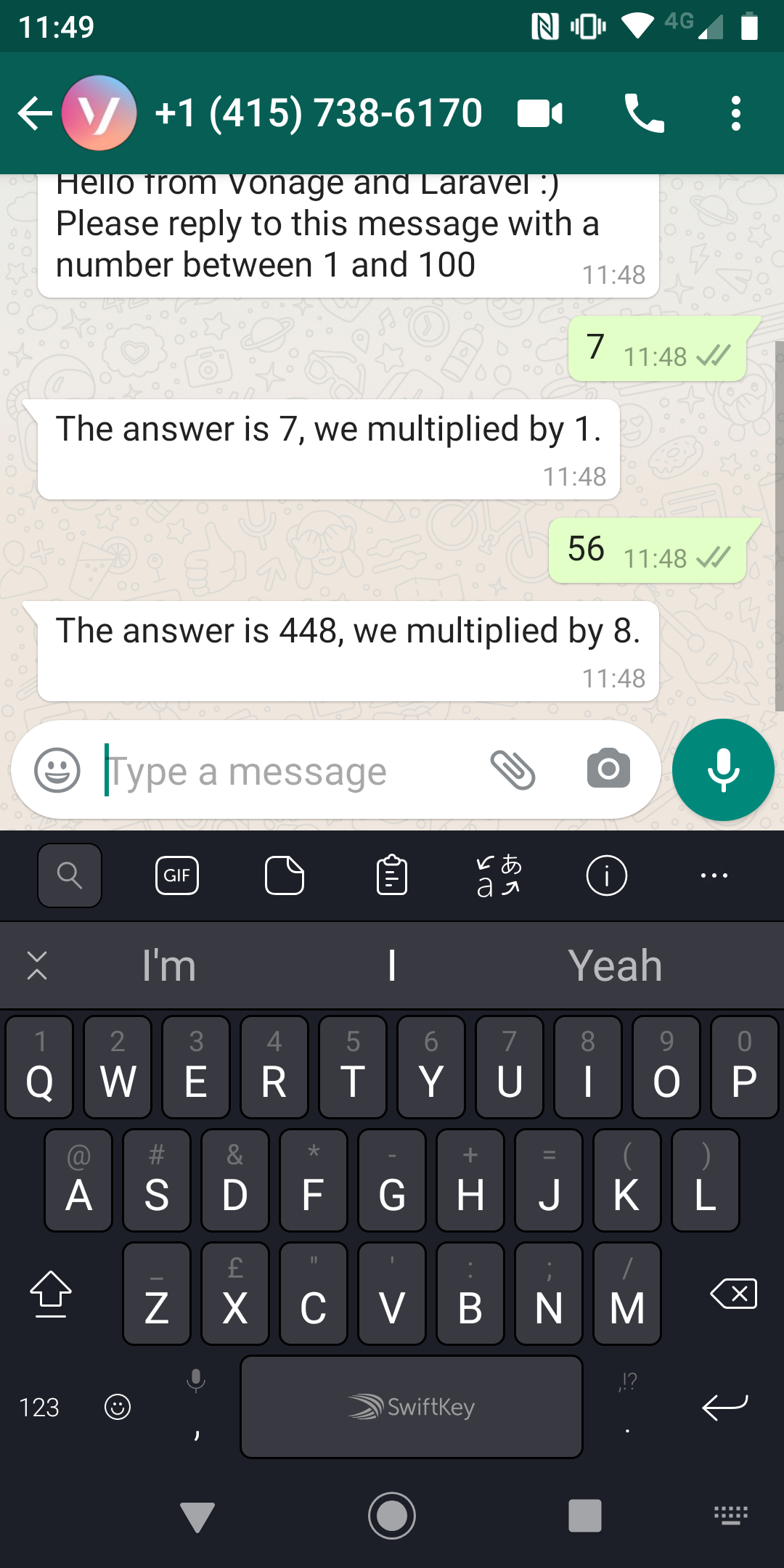
Today's example is simple but hopefully serves to get you started with WhatsApp and Laravel. We would love to know what you build, so let us know, and of course, always reach out to us if you have questions!
More Resources
- GitHub repo: https://github.com/nexmo-community/laravel-messages
- The day we built this on our Twitch Stream: https://youtu.be/aV4IW3v-CTw
- Documentation for Messages Sandbox: https://developer.nexmo.com/messages/concepts/messages-api-sandbox
- The
nexmo-laravellibrary for integrating your Laravel application with other Vonage APIs https://github.com/Nexmo/nexmo-laravel
