
Using Dialogflow with Firebase and the Vonage Messages Sandbox
Using Dialogflow to build a chatbot to interact with your customer is a great way to handle incoming requests like reservations, bank inquiries, FAQs, and initial support. When you combine Dialogflow with Firebase and Vonage Messages API, things start to heat up.
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you are connecting a Dialogflow agent with the Vonage Messages API using Firebase. When complete, you can send a message in Facebook Messenger to the Dialogflow agent and get a response based on the agent's rules.
You'll want to make sure you have:
Vonage API Account
To complete this tutorial, you will need a Vonage API account. If you don’t have one already, you can sign up today and start building with free credit. Once you have an account, you can find your API Key and API Secret at the top of the Vonage API Dashboard.
This tutorial also uses a virtual phone number. To purchase one, go to Numbers > Buy Numbers and search for one that meets your needs.
Create a Firebase Application
If this is your first time setting up a Firebase project, I would recommend you work through Google's Firebase getting started tutorial first to get yourself acclimated to the environment. If you are accustomed to Firebase or feeling adventurous, the first step is to create a new Firebase project. Feel free to name this anything memorable.
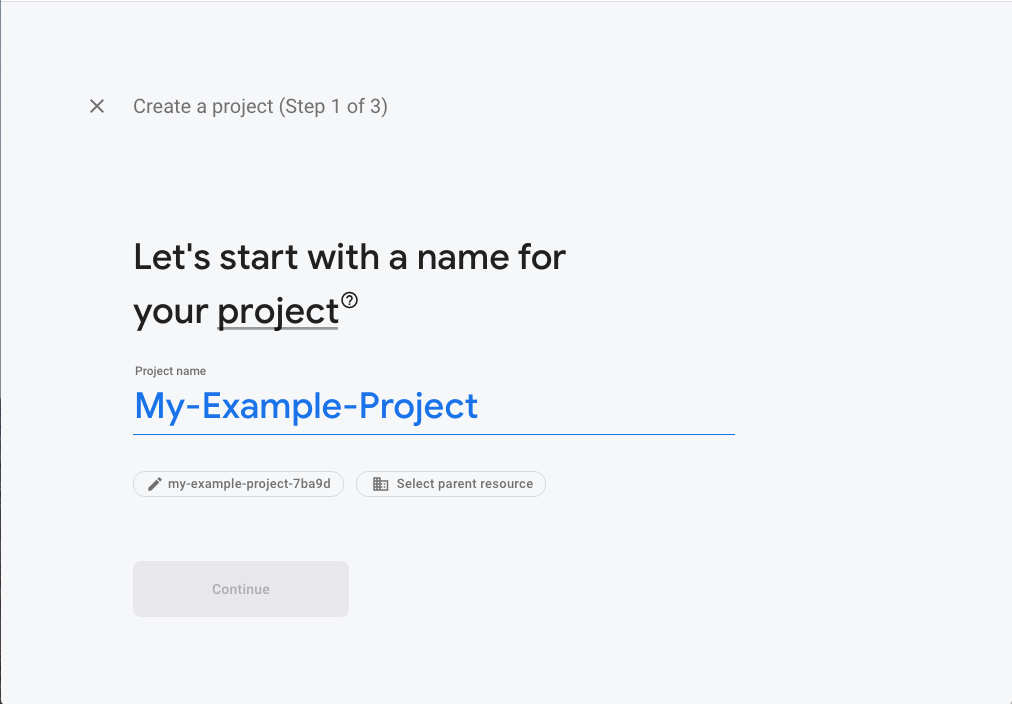
Once through the initial creation process (less than 5 minutes), set up these two items in the dashboard of your project:
- Upgrade to Blaze Pay-As-You-Go You can locate this under Settings -> Usage and Billing -> Details & Settings -> Modify Plan. Firebase requires Blaze for any 3rd party integrations to work.
- Pick a Resource Location Find this in Settings -> Project Settings -> General
Once those are all set, you can set up the Dialogflow agent and associate it with the new Firebase/GCP project.
Set Up Dialogflow Agent
Now you are ready to create a new Dialogflow agent—the chatbot that you will be interacting with later. Dialogflow uses Natural Language Processing to determine the user's intents based on what they type or speak and return an action based on that intent.
Next, import a "Prebuilt Agent" provided by Google to help get you started. If you are new to DialogFlow, you need to create a blank agent on the landing page.
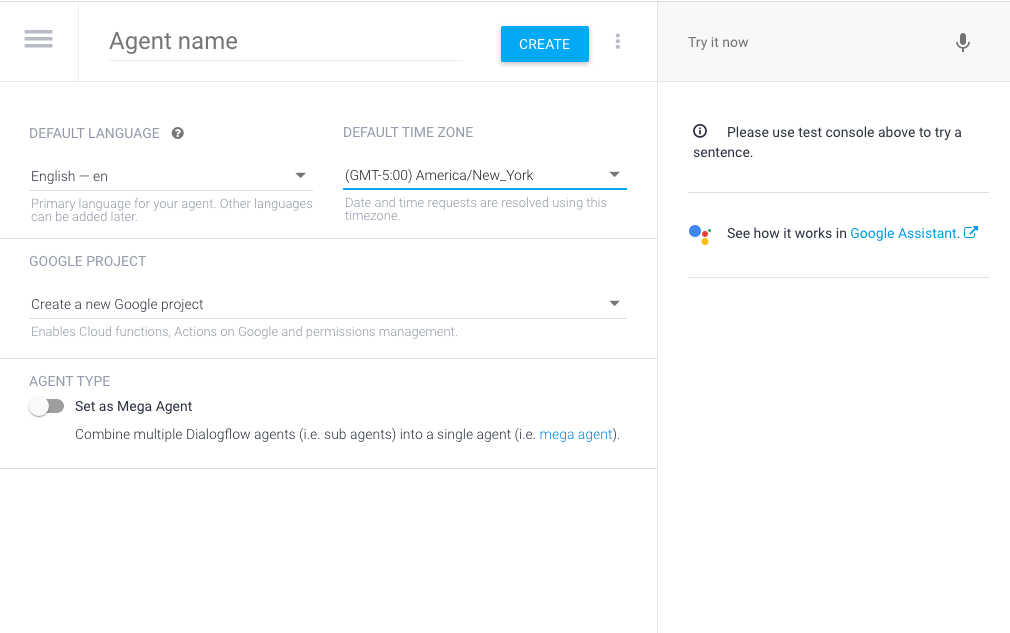
Once you have an agent, you can select the "Prebuilt Agents" from the left menu. You are presented with many different types of agents that might help you start learning how to build your chatbot. For this example, I picked "Easter Eggs."
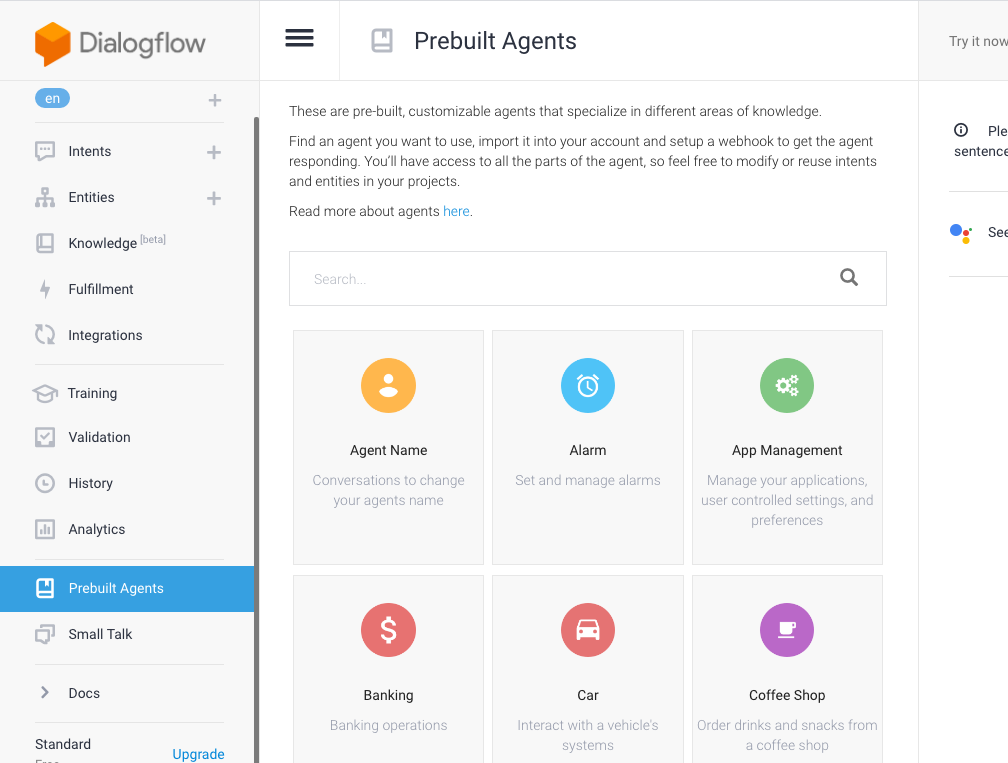
Import an agent and wait for it to complete the build process. Once finished, get the credentials for the service account.
Download Service Account Keys
Navigate to the GCP IAM & Admin service for service accounts. Make sure you select the correct project that you have been using already.
You should see a service account that looks similar to dialogflow@myexampleproject.iam.gserviceaccount.com. Click the dots on the right and select Create Key and then pick JSON from the options. This process generates and downloads a JSON file. Save this file for later.
Build Functions Locally
You now have a Firebase project and a Dialogflow agent ready to go. The two systems need to communicate with each other and with Vonage APIs. To do that, you need a little code to make things work.
The Firebase CLI has some helpful tools to get you started. Make sure you have the latest version and run the following:
firebase init functions
This command creates the project inside your root folder and asks you to connect it to an already existing project. After a few prompts, the command runs npm install to install all of the requirements. Once complete, navigate to the functions folder and use this command to install the other packages you need:
npm i @google-cloud/Dialogflow axios
At this time, you should also move the service account JSON file over to the functions directory. Once you've done that, make sure to add it to your .gitignore file as well.
The Code
Inside the functions directory is index.js. They provide some sample code to get you started, but you can delete and replace it with the following code to send a message to the Vonage Messages Sandbox. Make sure to have your Vonage API key and secret handy for this.
const functions = require('firebase-functions');
const axios = require('axios');
// the service account JSON file downloaded earlier - make sure this is named properly
const serviceAccount = require('./service_account.json');
const Dialogflow = require('@google-cloud/Dialogflow');
// This method takes the TO_ID, FROM_ID, MSG from the webhook defined later
// DialogFlow responses will be sent using this function
// You will need to get your API Key and Secret from the Vonage Dashboard.
function sendMessage(TO_ID, FROM_ID, MSG) {
return axios.post('https://messages-sandbox.nexmo.com/v0.1/messages', {
"from": { "type": 'messenger', "id": FROM_ID },
"to": { "type": 'messenger', "id": TO_ID },
"message": {
'content': {
'type': 'text',
'text': MSG
}
}
}, {
auth: {
username: 'API_KEY',
password: 'API_SECRET'
}
})
}
The next function is the gateway between Firebase and Dialogflow. The incoming message from Vonage is sent to the Dialogflow agent to determine the intent of the message. Once the intent is determined, Dialogflow passes back a message to forward on to the client.
async function DialogflowGateway(text, sessionId) {
const sessionClient = new Dialogflow.SessionsClient({ credentials: serviceAccount });
const sessionPath = sessionClient.projectAgentSessionPath('YOUR-GOOGLE-PROJECT', sessionId);
const request = {
session: sessionPath,
queryInput: {
text: {
text: text,
languageCode: 'en-US',
},
},
};
console.log(request)
return sessionClient.detectIntent(request);
}
The Vonage Messages Sandbox uses an inbound webhook to receive the messages using a POST method to Firebase.
exports.webhook = functions.https.onRequest(async (req, res) => {
const { message, from, to } = req.body;
try {
// the message from the user is sent to Dialogflow, and a response is returned
const response = await DialogflowGateway(message.content.text, from.id);
// the response from Dialogflow is sent back to the user through Vonage
await sendMessage(from.id, to.id, response[0].queryResult.fulfillmentText);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
res.sendStatus(200);
});
These three functions should be inside the index.js file and saved. All that is left is to deploy these functions.
Deploy Functions
Using the Firebase CLI, deploy the functions to Firebase using this command:
firebase deploy --only functions
On successful deployment, you get the webhook required for the Vonage Messages Sandbox Inbound webhook.
✔ functions: Finished running predeploy script.
i functions: ensuring required API cloudfunctions.googleapis.com is enabled...
✔ functions: required API cloudfunctions.googleapis.com is enabled
i functions: preparing functions directory for uploading...
i functions: packaged functions (47.86 KB) for uploading
✔ functions: functions folder uploaded successfully
i functions: creating Node.js 8 function webhook(us-central1)...
✔ functions[status(us-central1)]: Successful create operation.
✔ functions[webhook(us-central1)]: Successful create operation.
Function URL (webhook): https://us-central1-myexampleproject.cloudfunctions.net/webhook
✔ Deploy complete!
Once you have the webhook updated, you can test it out on Facebook Messenger.
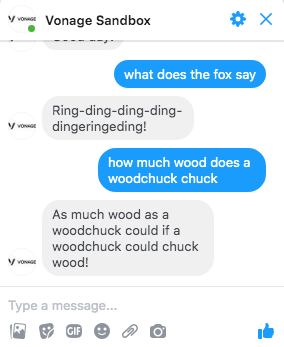
Feel free to change intents and actions in Dialogflow to start to see how it can work in your communication strategy.
If you'd like to see a full version of this and other Google Cloud examples, you can find it here - https://github.com/nexmo-community/google-cloud-sample-code. If you have any questions or requests for other examples with Google Cloud, Dialogflow or Firebase, open up a pull request or shoot me a message on Twitter.
