AWS Lambda With PHP Using Bref And Serverless Framework
Using PHP in serverless environments has previously been challenging due to the lack of default runtimes provided by the various cloud providers. However, this has changed recently with added libraries and functionality, making the use of PHP more approachable.
This example will create an AWS Lambda Function for PHP using Bref. The addition of AWS Lambda Runtime API and the ability to add AWS Lambda Layers has made it easier to create a PHP custom runtime. Therefore, packages like Bref have sprung up to make PHP developers' lives easier.
Prerequisites
Here are things you will need for this example:
- PHP installed locally (version 7.3+ preferred)
- Composer installed globally
- Node.js
- AWS account and access keys for a user with access to AWS S3 as well as AWS Lambda
Serverless Framework
The Bref tool leverages the Serverless Framework foundation, which is a "complete solution for building and operating serverless applications". Thus, our first step is to get this framework installed on the development system you're using. We recommend installing it globally, to allow usage from anywhere via CLI.
npm install -g serverless
AWS Credentials
With Serverless installed, ensure you've also set up the AWS credentials needed for Serverless to interact with the various AWS services. (S3, Lambda, and potentially EC2 or databases as required) In this example, we will only be using S3 and Lambda. You can read more about this at serverless.com and bref.sh so that we won't go into the details here.
Install Bref
You should also install Bref as a dependency within each given project using it. With that in mind, we will use Composer to install it using the CLI from within the project directory.
composer require bref/bref
Init Bref Project
After Composer has finalized the addition of Bref to the project, the best way to get started is to init Bref for usage. Doing the init will then prompt whether you desire a Function, HTTP, or Console function, resulting in the creation of serverless.yml and possibly index.php depending upon your selection, which you can edit to fit the needs of the application.
vendor/bin/bref init
Example YML File
As an example, below is a sample serverless.yml file:
service: app
provider:
name: aws
region: us-east-1
runtime: provided
plugins:
- ./vendor/bref/bref
functions:
function:
handler: index.php
description: ''
layers:
- ${bref:layer.php-73}
# Exclude files from deployment
package:
exclude:
- 'tests/**'
In the file, observe the name of the service, which you can alter to fit the desired naming conventions of your functions. By default, it is named app.
Following this, we can see the provider information for AWS Lambda.
There is a section for any plugins and the inclusion of Bref.
Then, there is the section outlining the details of the function. Included is the handler, desired description to be added to AWS, and any layers required, such as PHP. Note in the example above, php-73 is specified. If you selected HTTP instead, it would specify php-73-fpm and provide a web server in the layer instead of a CLI only version of PHP. The image to be used is why the init process is essential to ensure Lambda creates the correct layer.
Deploying to AWS Lambda
For either Function or HTTP use cases, the default init provides enough of a skeleton to deploy straight to AWS Lambda and test using Serverless. Leveraging the AWS credentials configuration added prior, Serverless will deploy straight to Lambda using the contents of serverless.yml as criteria.
serverless deploy
IMPORTANT: The example application, as-is, does not carry any authentication or verification. Anyone with access to the URL provided after deployment can access it. Doing so could cause unexpected charges to your accounts. Therefore, please secure the app if you intend to leave it active.
Testing the Function
In the case of a function, there are two ways to test. One way is to use the AWS Console, while the second is using Serverless via CLI from the system used to deploy.
AWS Console
By navigating the AWS Console select the Lambda item from the list of Compute services.

On the Lambda dashboard, you can select the function created and create a new test by clicking Configure test events. Alternatively, you can click the Test button to receive the same prompt.
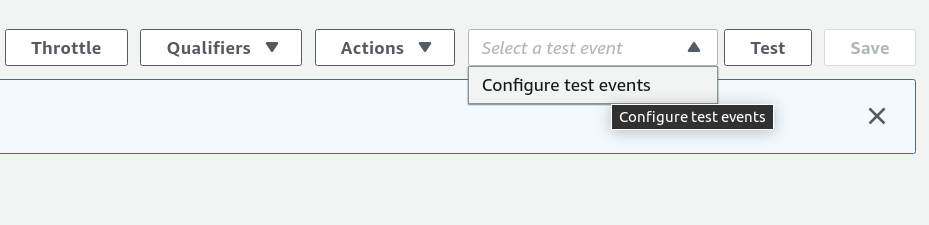
For a test of the skeleton created, add a name and slightly alter the JSON in the body.
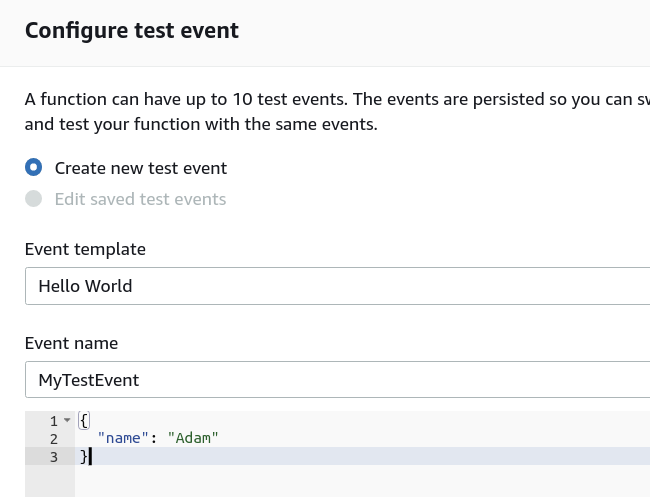
Upon clicking the Create button at the bottom of the dialog, you can then click the Test button to execute the test. Running should result in a green dialog area you can expand to show the results.
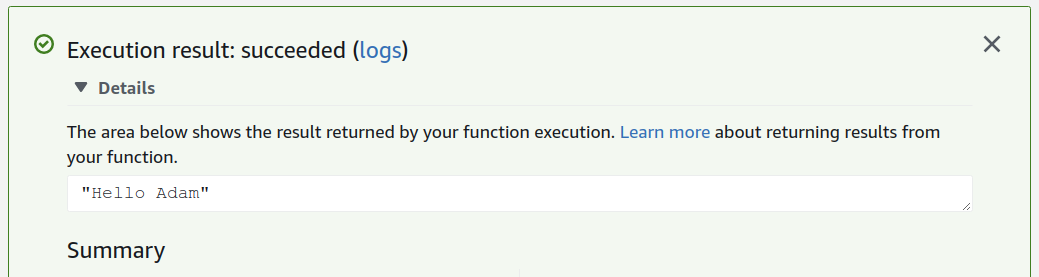
Serverless Function Execution
As stated above, you can also use the Serverless CLI to also test the function by using the following command from within the local application root:
serverless invoke -f function --data='{"name": "Adam"}'
Example result:
Testing An HTTP Function
If you deployed an HTTP function instead, the two testing methods above would not work. Instead, you can use an HTTP client or a standard browser to test by using the URL provided by the deploy output results.
What Next
With an AWS Lambda function created, you can continue adding more code and creating more robust PHP apps leveraging the serverless technologies available today. Watch for future posts showing how to build useful functions to leverage Vonage APIs and services using AWS Lambda.